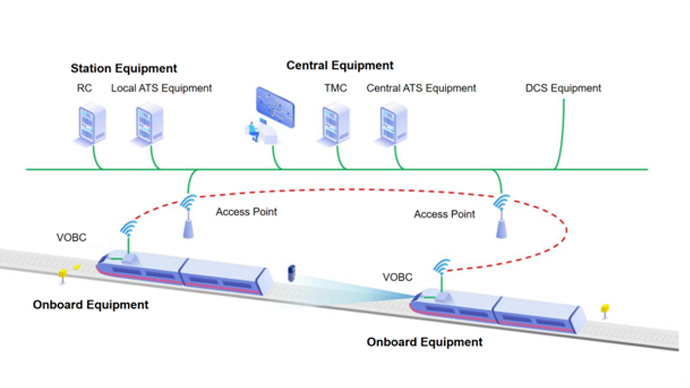
Background
Amidst the rapid development of urban rail transit, traditional train control systems face challenges such as complex system architecture, numerous ground-based equipment, lengthy installation and commissioning periods, limited transport efficiency, and high construction and maintenance costs. Meanwhile, high-density train operation and complex environments impose higher demandson resource utilization, traffic density, operational resilience, and safety of train control systems. Therefore, it has become an urgent industry need to develop a train control system that features simplified architecture, minimal ground equipment, short installation and commissioning time, high transport efficiency, low construction and maintenance costs, and robust safety and resilience.




