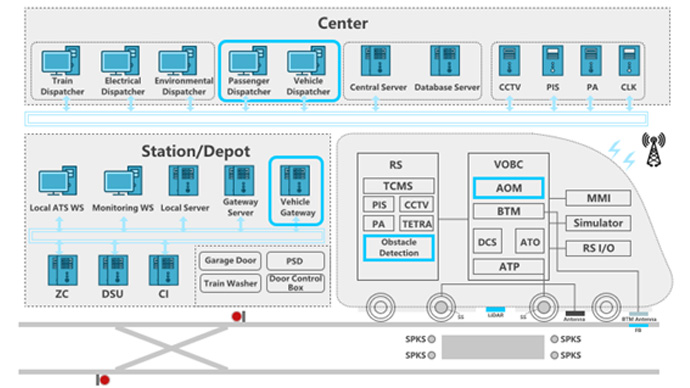
Background
The rapid development of urban rail transit has imposed higher requirements on train operation systems. Traditional systems, which rely heavily on manual operation, face issues such ashigh risks of human error and low operational efficiency. In this case, it has become an inevitable trend to develop FAO systems that feature high integration, advanced automation, sound safety protection, and flexible operational management.
Relevant policy documentsissued by the Ministry of Transport, international standards (including IEC 62290), and industry specifications (includingT/CAMET 04016 & 04017) provide guidance for the development of FAO systems, supporting the standardized and orderly advancement of the industry.




